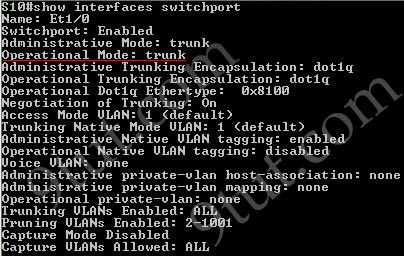
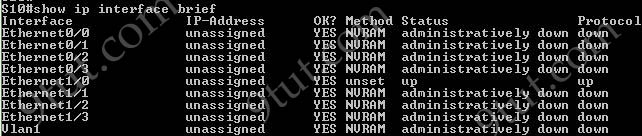
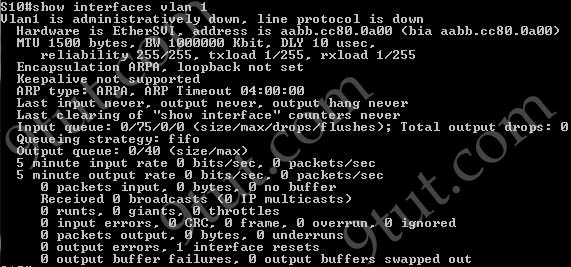
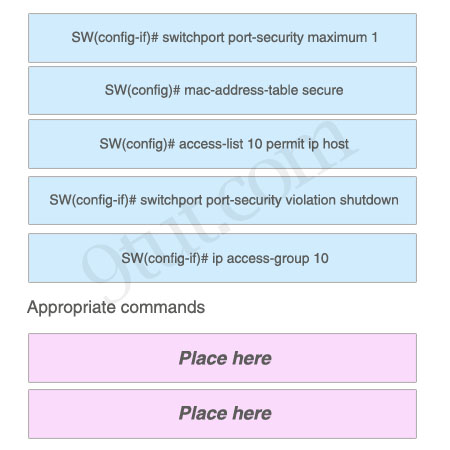
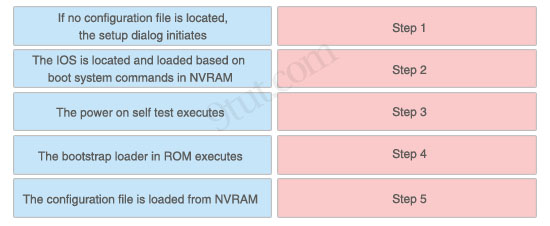
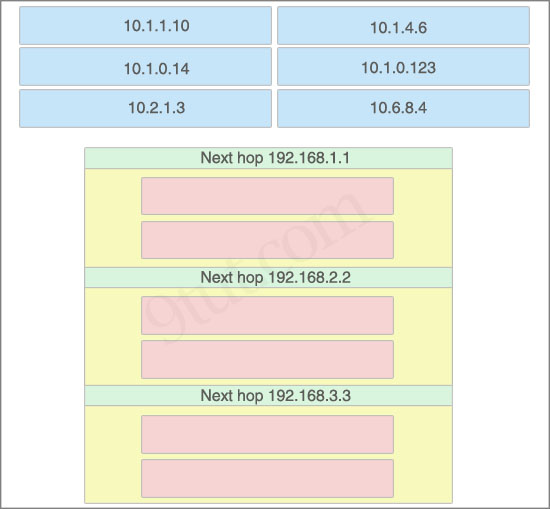
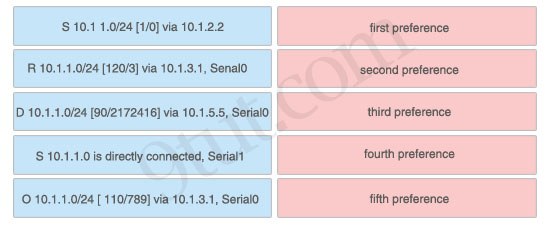
Here you will find answers to CCNA hotspot Questions
Hotspot Routing Question
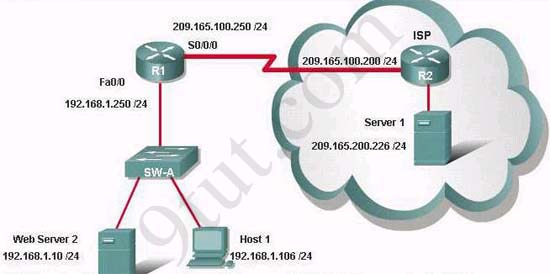
A – R1 will forward the packet out all interfaces
B – R1 will drop this packet because it is not a valid IP address
C – As R1 forwards the frame containing this packet, Sw-A will add 192.168.1.255 to its MAC table
D – R1 will encapsulate the packet in a frame with a destination MAC address of FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF
E – As R1 forwards the frame containing this packet, Sw-A will forward it ti the device assigned the IP address of 192.168.1.255
Answer: B
A – ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0
B – ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.200.226
C – ip route 209.165.200.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.250
D – ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 209.165.100.250
Answer: A
A – 0
B – 1
C – 2
D – 3
E – 4
Answer: C or D(depending on your understand, please read the comments to understand why)
A – On router R2,configure a default static route to the 192.168.1.0 network
B – On router r2, configure DNS to resolve the URL assigned to Web Server 2 to the 192.168.1.10 address
C – On router R1, configure NAT to translate an address on the 209.165.100.0/24 network to 192.168.1.10
D – On router R1, configure DHCP to assign a registered IP address on the 209.165.100.0/24 network to Web Server 2
Answer: C
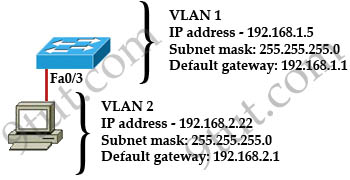
A – 255.255.255.0
B – 255.255.255.192
C – 255.255.255.250
D – 255.255.255.252
Answer: A
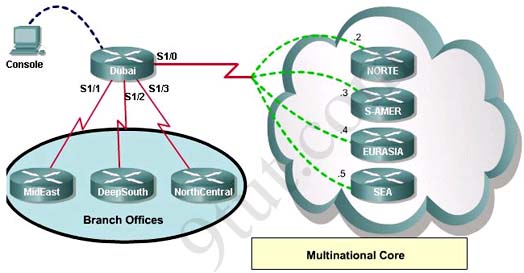
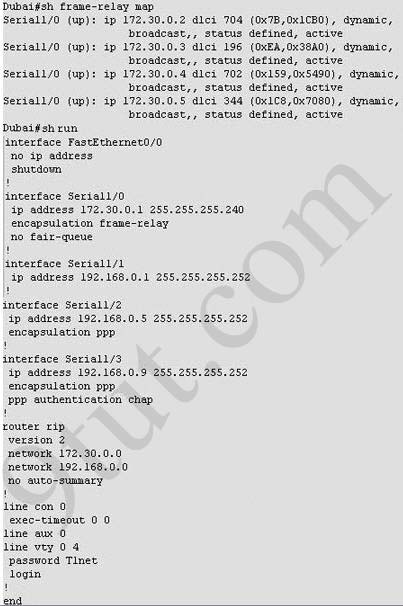 (In the old days, this question was a multi-choice question but Cisco
upgraded it into a lab-sim question. Therefore, instead of listing all
the configuration as above, you have to type show frame-relay map and show running-config to get its configuration)
(In the old days, this question was a multi-choice question but Cisco
upgraded it into a lab-sim question. Therefore, instead of listing all
the configuration as above, you have to type show frame-relay map and show running-config to get its configuration)
Note: If you are not sure about Frame-Relay, please read my Frame Relay tutorial.
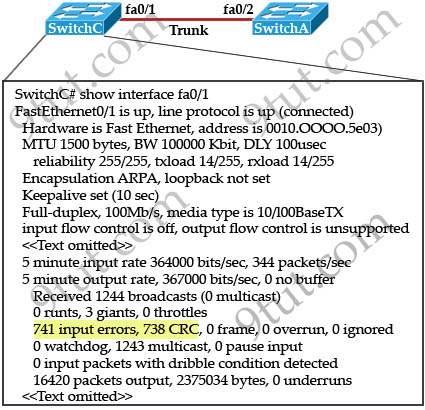
A – 704
B – 196
C – 702
D – 344
Answer: C
A – frame-relay map ip 172.30.0.3 704 broadcast
B – frame-relay map ip 172.30.0.3 196 broadcast
C – frame-relay map ip 172.30.0.3 702 broadcast
D – frame-relay map ip 172.30.0.3 344 broadcast
Answer: B
A – The serial connection to the MidEast branch office
B – The serial connection to the DeepSouth branch office
C – The serial connection to the NorthCentral branch office
D – The serial connection to the Multinational Core
Answer: A
A – No password is required
B – Enable
C – Scr
D – Telnet
E – Console
Answer: A or D (because maybe there are 2 versions of this question, depending on the output of “show running-config” command, please read the explanation below)
Explanation
This question is not clear for a long time but now maybe the trick was solved. What Cisco wants to ask is the word used as password, not the type of connection, so in the exam you might see some strange words for answers like “En8ble”, “T1net”, “C0nsole”. All you have to do is to use the command “show running-config” as wx4 mentioned below to find the answer.
wx4 commented:
Q4: if password required which?
in my example it was connection to North!
How to figure out which pw is required?
#show running-config
1. check the interface to the router you need connection to. If there is “ppp authentication” you need a password!
2. you will find the password on the top of your running-config output
check the area:
username North password c0nsole
username xxxxx yyyyy
username…
in my case it was c0nsole, in your case it can be no password needed or a different password.
If you are still not clear, please read anton‘s comment:
A big question I noticed here was about the FR Lab regarding the password. You have to perform a show running-config and look for USERNAME and PASSWORD.
i.e.
username South_Router password c0nsol3
username North_Router password t31net
Obviously this has to be en PPP encapsulation, if asked for a posible password for SOUTH_ROUTER you pick c0nsol3, and for NORTH_ROUTER you pick t31net. If you’re running HDLC, i would pick “no password is required”.
Hotspot Routing Question


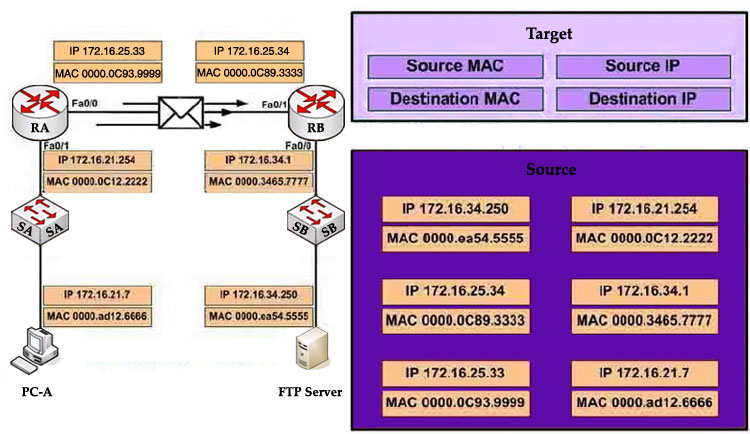
Question 1:
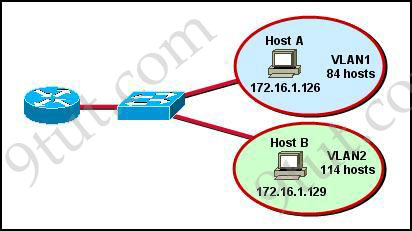
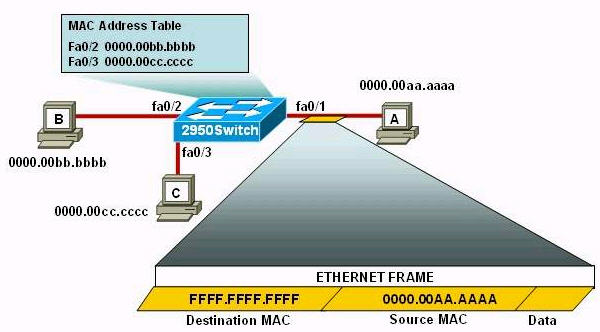
If the router R1 has a packet with a destination address 192.168.1.255, what describes the operation of the network?A – R1 will forward the packet out all interfaces
B – R1 will drop this packet because it is not a valid IP address
C – As R1 forwards the frame containing this packet, Sw-A will add 192.168.1.255 to its MAC table
D – R1 will encapsulate the packet in a frame with a destination MAC address of FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF
E – As R1 forwards the frame containing this packet, Sw-A will forward it ti the device assigned the IP address of 192.168.1.255
Answer: B
Question 2:
Users on the 192.168.1.0/24 network must access files located on the
Server 1. What route could be configured on router R1 for file requests
to reach the server?A – ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0
B – ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.200.226
C – ip route 209.165.200.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.250
D – ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 209.165.100.250
Answer: A
Quetion 3:
When a packet is sent from Host 1 to Server 1, in how many different
frames will the packet be encapsulated as it is sent across the
internetwork?A – 0
B – 1
C – 2
D – 3
E – 4
Answer: C or D(depending on your understand, please read the comments to understand why)
Question 4:
What must be configured on the network in order for users on the Internet to view web pages located on Web Server 2?A – On router R2,configure a default static route to the 192.168.1.0 network
B – On router r2, configure DNS to resolve the URL assigned to Web Server 2 to the 192.168.1.10 address
C – On router R1, configure NAT to translate an address on the 209.165.100.0/24 network to 192.168.1.10
D – On router R1, configure DHCP to assign a registered IP address on the 209.165.100.0/24 network to Web Server 2
Answer: C
Question 5:
The router address 192.168.1.250 is the default gateway for both the
Web Server 2 and Host 1. What is the correct subnet mask for this
network?A – 255.255.255.0
B – 255.255.255.192
C – 255.255.255.250
D – 255.255.255.252
Answer: A
Hotspot Frame-relay Question


Note: If you are not sure about Frame-Relay, please read my Frame Relay tutorial.
Question 1:
What destination Layer 2 address will be used in the frame header containing a packet for host 172.30.0.4?A – 704
B – 196
C – 702
D – 344
Answer: C
Question 2:
A static map to the S-AMER location is required. Which command should be used to create this map?A – frame-relay map ip 172.30.0.3 704 broadcast
B – frame-relay map ip 172.30.0.3 196 broadcast
C – frame-relay map ip 172.30.0.3 702 broadcast
D – frame-relay map ip 172.30.0.3 344 broadcast
Answer: B
Question 3:
Which connection uses the default encapsulation for serial interfaces on Cisco routers?A – The serial connection to the MidEast branch office
B – The serial connection to the DeepSouth branch office
C – The serial connection to the NorthCentral branch office
D – The serial connection to the Multinational Core
Answer: A
Question 4:
If required, what password should be configured on the router in the
MidEast branch office to allow a connection to be established with the
Dubai router?A – No password is required
B – Enable
C – Scr
D – Telnet
E – Console
Answer: A or D (because maybe there are 2 versions of this question, depending on the output of “show running-config” command, please read the explanation below)
Explanation
This question is not clear for a long time but now maybe the trick was solved. What Cisco wants to ask is the word used as password, not the type of connection, so in the exam you might see some strange words for answers like “En8ble”, “T1net”, “C0nsole”. All you have to do is to use the command “show running-config” as wx4 mentioned below to find the answer.
wx4 commented:
Q4: if password required which?
in my example it was connection to North!
How to figure out which pw is required?
#show running-config
1. check the interface to the router you need connection to. If there is “ppp authentication” you need a password!
2. you will find the password on the top of your running-config output
check the area:
username North password c0nsole
username xxxxx yyyyy
username…
in my case it was c0nsole, in your case it can be no password needed or a different password.
If you are still not clear, please read anton‘s comment:
A big question I noticed here was about the FR Lab regarding the password. You have to perform a show running-config and look for USERNAME and PASSWORD.
i.e.
username South_Router password c0nsol3
username North_Router password t31net
Obviously this has to be en PPP encapsulation, if asked for a posible password for SOUTH_ROUTER you pick c0nsol3, and for NORTH_ROUTER you pick t31net. If you’re running HDLC, i would pick “no password is required”.