Here you will find answers to TCP/IP Model & Operation Questions
A. FTP
B. Telnet
C. SMTP
D. DNS
E. HTTP
F. POP3
Answer: D E F
A. It sends data in clear text format.
B. It is no longer supported on Cisco network devices.
C. It is more secure than SSH.
D. It requires an enterprise license in order to be implemented.
E. It requires that the destination device be configured to support Telnet connections.
Answer: A E
The destination device needs to support Telnet connection. For example, if a device doesn’t support TCP/IP protocol suit then maybe we can’t telnet to it.
A. The PC has connectivity with a local host.
B. The PC has connectivity with a Layer 3 device.
C. The PC has a default gateway correctly configured
D. The PC has connectivity up to Layer 5 of the OSI model
E. The PC has the TCP/IP protocol stack correctly installed.
Answer: E
A. application
B. internet
C. network
D. transport
Answer: B
A. Drop the data.
B. Send the data frames to the default gateway.
C. Create an ARP request to get a MAC address for the receiving host.
D. Send a TCP SYN and wait for the SYN ACK with the IP address of the receiving host.
Answer: B
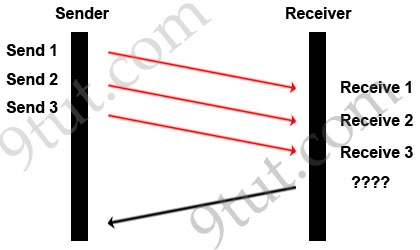
A window size of three has been negotiated for this transfer. Which message will be returned from the receiver to the sender as part of this TCP/IP transfer?
 A. Send ACK 1-3
A. Send ACK 1-3
B. Send ACK 3
C. Send ACK 4
D. Send ACK 4-6
E. Send ACK 6
F. Send ACK 7
Answer: C
Explanation
In response, the receiver replies with an ACK. The acknowledgment number is set to one more than the received sequence number. The ACK means “I have got all messages up to sequence number n-1 so please send me the message for sequence number n”.
A. to map all the devices on a network.
B. to display the current TCP/IP configuration values.
C. to see how a device MAC address is mapped to its IP address.
D. to see the path a packet will take when traveling to a specified destination.
E. to display the MTU values for each router in a specified network path from source to a destination.
Answer: D
A. path cisco.com
B. debugcisco.com
C. trace cisco.com
D. traceroute cisco.com
Answer: D
 A. abcd.abcd.a001
A. abcd.abcd.a001
B. abcd.abcd.b002
C. abcd.abcd.c003
D. 10.2.0.15
E. 10.0.64.1
F. 10.0.128.15
Answer: B D
+ Source IP: IP of Host A - 10.2.0.15 (never changed)
+ Destination IP: IP of Host B – 10.0.128.15 (never changed)
+ Source MAC: MAC of Fa0/0 of R2 – abcd.abcd.b002
+ Destination MAC: MAC of Host B – abcd.abcd.d004
 A. Router C will use ICMP to inform Host 1 that Host 2 cannot be reached.
A. Router C will use ICMP to inform Host 1 that Host 2 cannot be reached.
B. Router C will use ICMP to inform Router B that Host 2 cannot be reached.
C. Router C will use ICMP to inform Host 1, Router A, and Router B that Host 2 cannot be reached.
D. Router C will send a Destination Unreachable message type.
E. Router C will send a Router Selection message type.
F. Router C will send a Source Quench message type.
Answer: A D
 A. The MAC address of host A is FFFF.FFFF.FFFF.
A. The MAC address of host A is FFFF.FFFF.FFFF.
B. The router will forward the packet in this frame to the Internet.
C. The switch will only forward this frame to the attached router interface.
D. All devices in this LAN except host A will pass the packet to Layer 3.
Answer: D
Just for your information, maybe you can ask “this is a broadcast message so why router R1 doesn’t drop it?”. Suppose this is an ARP Request message. In fact, R1 drops that packet but it also learns that it is an ARP Request so R1 looks up its routing table to find a route to that destination. If it can find one, it will send an ARP Reply back for host A”.
Question 1
An inbound access list has been configured on a serial interface to
deny packet entry for TCP and UDP ports 21, 23 and 25. What types of
packets will be permitted by this ACL? (Choose three)A. FTP
B. Telnet
C. SMTP
D. DNS
E. HTTP
F. POP3
Answer: D E F
Explanation
The access list denies packet entry for TCP & UDP -> all the
services on ports 21, 23 and 25 are disabled. Services on these ports
are FTP (port 21), Telnet (port 23), SMTP (port 25). Other services are
allowed so D E F are the correct answers.
Question 2
What are two characteristics of Telnet? (Choose two)A. It sends data in clear text format.
B. It is no longer supported on Cisco network devices.
C. It is more secure than SSH.
D. It requires an enterprise license in order to be implemented.
E. It requires that the destination device be configured to support Telnet connections.
Answer: A E
Explanation
Telnet, part of the TCP/IP protocol suite, is a virtual terminal
protocol that allows you to make connections to remote devices, gather
information, and run programs. Telnet is considered insecure because it
transfers all data in clear text -> A is correct.The destination device needs to support Telnet connection. For example, if a device doesn’t support TCP/IP protocol suit then maybe we can’t telnet to it.
Question 3
An administrator issues the command ping 127.0.0.1 from the command
line prompt on a PC. If a reply is received, what does this confirm?A. The PC has connectivity with a local host.
B. The PC has connectivity with a Layer 3 device.
C. The PC has a default gateway correctly configured
D. The PC has connectivity up to Layer 5 of the OSI model
E. The PC has the TCP/IP protocol stack correctly installed.
Answer: E
Explanation
The address 127.0.0.1 is called loopback address. When we ping
127.0.0.1, in fact we are pinging the local network card and test the
TCP/IP protocol suite on our device.
Question 4
Where does routing occur within the DoD TCP/IP reference model?A. application
B. internet
C. network
D. transport
Answer: B
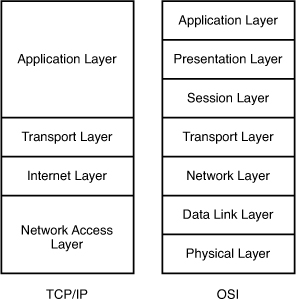
Explanation
The picture below shows the comparison between TCP/IP model & OSI
model. Notice that the Internet Layer of TCP/IP is equivalent to the
Network Layer which is responsible for routing decision.
Question 5
A host is attempting to send data to another host on a different
network. What is the first action that the sending host will take?A. Drop the data.
B. Send the data frames to the default gateway.
C. Create an ARP request to get a MAC address for the receiving host.
D. Send a TCP SYN and wait for the SYN ACK with the IP address of the receiving host.
Answer: B
Explanation
Before sending data, the sending host checks if the destination host
is inside or outside the local network. If it is outside the local
network, the data will be sent to the default gateway.
Question 6
A TCP/IP Transfer is diagrammed in the exhibit.A window size of three has been negotiated for this transfer. Which message will be returned from the receiver to the sender as part of this TCP/IP transfer?

B. Send ACK 3
C. Send ACK 4
D. Send ACK 4-6
E. Send ACK 6
F. Send ACK 7
Answer: C
Explanation
In response, the receiver replies with an ACK. The acknowledgment number is set to one more than the received sequence number. The ACK means “I have got all messages up to sequence number n-1 so please send me the message for sequence number n”.
Question 7
What is the purpose using the traceroute command?A. to map all the devices on a network.
B. to display the current TCP/IP configuration values.
C. to see how a device MAC address is mapped to its IP address.
D. to see the path a packet will take when traveling to a specified destination.
E. to display the MTU values for each router in a specified network path from source to a destination.
Answer: D
Question 8
A network admin wants to know every hop the packets take when he
accesses cisco.com. Which command is the most appropriate to use?A. path cisco.com
B. debugcisco.com
C. trace cisco.com
D. traceroute cisco.com
Answer: D
Question 9
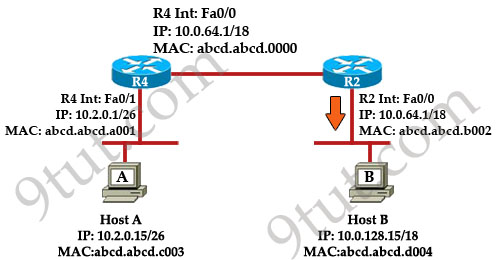
Refer to the exhibit. Host A pings Host B. What source MAC address
and source IP address are contained in the frame as the frame leaves R2
destined for host B?
B. abcd.abcd.b002
C. abcd.abcd.c003
D. 10.2.0.15
E. 10.0.64.1
F. 10.0.128.15
Answer: B D
Explanation
When packets are sent from Host A to Host B, the source and
destination IP addresses are never changed and they are the IP addresses
of Host A & Host B. Only the MAC addresses will be changed to
reflect the device of the current network. In this case, when the frame
leaves R2 destined for host B. It will have:+ Source IP: IP of Host A - 10.2.0.15 (never changed)
+ Destination IP: IP of Host B – 10.0.128.15 (never changed)
+ Source MAC: MAC of Fa0/0 of R2 – abcd.abcd.b002
+ Destination MAC: MAC of Host B – abcd.abcd.d004
Question 10
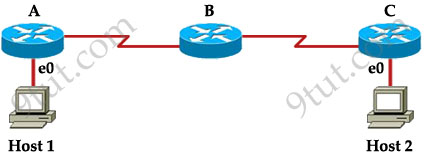
Host 1 is trying to communicate with Host 2. The e0 interface on Router C is down. Which of the following are true? (Choose two)
B. Router C will use ICMP to inform Router B that Host 2 cannot be reached.
C. Router C will use ICMP to inform Host 1, Router A, and Router B that Host 2 cannot be reached.
D. Router C will send a Destination Unreachable message type.
E. Router C will send a Router Selection message type.
F. Router C will send a Source Quench message type.
Answer: A D
Explanation
The last known good router will try to inform you that the
destination cannot be reached (with a Destination Unreachable message
type) so from that information you can learn how far your packets can
travel to and where the problem is.
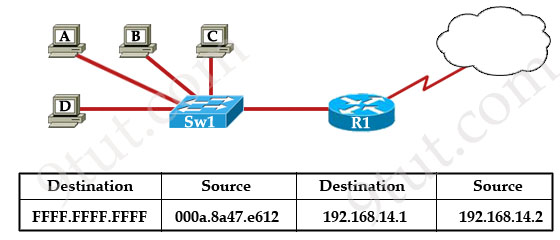
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit. The switch in the graphic has a default
configuration and the MAC table is fully populated. In addition, this
network is operating properly. The graphic represents selected header
information in a frame leaving host A. What can be concluded from this
information?
B. The router will forward the packet in this frame to the Internet.
C. The switch will only forward this frame to the attached router interface.
D. All devices in this LAN except host A will pass the packet to Layer 3.
Answer: D
Explanation
This frame is leaving host A so host A is the source of this frame.
In this frame, the MAC destination is FFFF.FFFF.FFFF which is a
broadcast address so Sw1 will flood this frame out all its ports except
the port it received the frame -> Hosts B, C, D and the interface
connected to Sw1 on R1 will receive this frame. When receiving this
frame, they will pass the packet to Layer 3 (because they consider
broadcast address “everyone, including me”). At Layer 3, the Destination
IP will be checked and only the host (or the interface on the router)
with correct IP will respond to Host A while others keep silence -> D
is correct.Just for your information, maybe you can ask “this is a broadcast message so why router R1 doesn’t drop it?”. Suppose this is an ARP Request message. In fact, R1 drops that packet but it also learns that it is an ARP Request so R1 looks up its routing table to find a route to that destination. If it can find one, it will send an ARP Reply back for host A”.
No comments:
Post a Comment