Here you will find answers to IP Routing Questions – Part 2
 A. Router1 will strip off the source MAC address and replace it with the MAC address on the forwarding FastEthernet interface.
A. Router1 will strip off the source MAC address and replace it with the MAC address on the forwarding FastEthernet interface.
B. Router1 will strip off the source IP address and replace it with the IP address on the forwarding FastEthernet interface.
C. Router1 will strip off the destination MAC address and replace it with the MAC address of Host B.
D. Router1 will strip off the destination IP address and replace it with the IP address of Host B.
E. Router1 will forward the data frame out interface FastEthernet0/1.
F. Router1 will forward the data frame out interface FastEthernet0/2.
Answer: A C F
A. to provide routing to a local web server
B. to provide routing from an ISP to a stub network
C. to provide routing that will override the configured dynamic routing protocol
D. to provide routing to a destination that is not specified in the routing table and which is outside the local network
Answer: D
Router(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.1
(Notice that the network address of default route is 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0)
All three routers are using RIP version 1.
The company network is using the block of 198.133.219.0/24.
The company has decided it would be a good idea to split the network into three smaller subnets and create the option of conserving addresses with VLSM.
What is the best course of action if the company wants to have 40 hosts in each of the three subnets?
A. Convert all the routers to EIGRP and use 198.133.219.32/27, 198.133.219.64/27, and 198.133.219.92/27 as the new subnetworks.
B. Maintain the use of RIP version 1 and use 198.133.219.32/27, 198.133.219.64/27, and 198.133.219.92/27 as the new subnetworks.
C. Convert all the routers to EIGRP and use 198.133.219.64/26, 198.133.219.128/26, and 198.133.219.192/26 as the new subnetworks.
D. Convert all the routers to RIP version 2 and use 198.133.219.64/26, 198.133.219.128/26, and 198.133.219.192/26 as the new subnetworks.
E. Convert all the routers to OSPF and use 198.133.219.16/28, 198.133.219.32/28, and 198.133.219.48/28 as the new subnetworks.
F. Convert all the routers to static routes and use 198.133.219.16/28, 198.133.219.32/28, and 198.133.219.48/28 as the new subnetworks.
Answer: D
But EIGRP is a Cisco-proprietary routing protocol so it can not be used in a non-Cisco router -> A and C are not correct.
To support 40 hosts per subnet we need a subnet mask of /26 or lower (which leaves 6 bits 0 and 26 = 64 > 40 hosts). Therefore a subnet mask of /28 is not suitable in this case -> E & F are not correct.
 A. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.2
A. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.2.2
B. ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.1
C. ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 s0/0/0
D. ip route 10:0.0.0 255.255.255.0 s0/0/0
E. ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.2
Answer: A
 A. The ip subnet-zero command has been issued on the R1 router.
A. The ip subnet-zero command has been issued on the R1 router.
B. The RIPv2 dynamic routing protocol cannot be used across a Frame Relay network.
C. Split horizon is preventing R2 from learning about the R3 networks and R3 from learning about R2 networks.
D. The 172.16.2.0/25 and 172.16.2.128/25 networks are overlapping networks that can be seen by R1, but not between R2 and R3.
E. The 172.16.3.0/29 network used on the Frame Relay links is creating a discontiguous network between the R2 and R3 router subnetworks.
Answer: C
 A. Configure the no ip subnet-zero command on R1, R2, and R3.
A. Configure the no ip subnet-zero command on R1, R2, and R3.
B. Dynamic routing protocols such as RIPv2 cannot be used across Frame Relay networks.
C. Configure the S0/0 interface on R1 as two subinterfaces and configure point-to-point links to R2 and R3.
D. Change the 172.16.2.0/25 and 172.16.2.128/25 subnetworks so that at least two bits are borrowed from the last octet.
E. Change the network address configuration to eliminate the discontiguous 172.16.2.0/25 and 172.16.2.128/25 subnetwork.
Answer: C
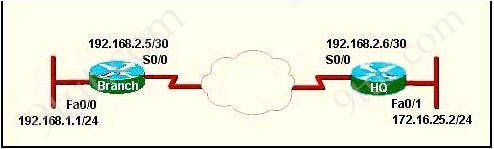 Which configuration will allow the hosts on the Branch LAN to access
resources on the HQ LAN with the least impact on router processing and
WAN bandwidth?
Which configuration will allow the hosts on the Branch LAN to access
resources on the HQ LAN with the least impact on router processing and
WAN bandwidth?
A.
HQ(config)# ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.5
Branch(config) # ip route 172.16.25.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.6
B.
HQ(config)# router rip
HQ(config-router)# network 192.168.2.0
HQ(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0
Branch(config)# router rip
Branch(config-router) # network 192.168.1.0
Branch(config-router)# network 192.168.2.0
C.
HQ(config)# router eigrp 56
HQ(config-router)# network 192.168.2.4
HQ(config-router)# network 172.16.25.0
Branch(config)# router eigrp 56
Branch(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0
Branch(config-router) # network 192.168.2.4
D.
HQ(config)# router ospf 1
HQ(config-router)# network 192.168.2.4 0.0.0.3 area 0
HQ(config-router)# network 172.16.25.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Branch(config)# router ospf 1
Branch(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Answer: A
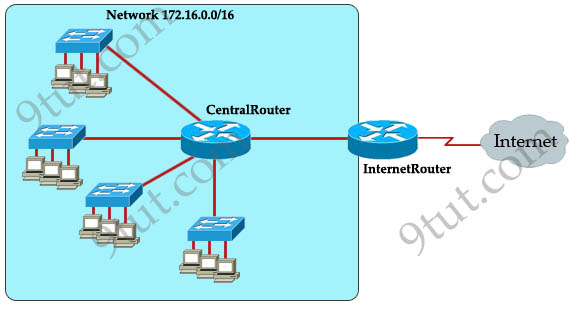 A. a dynamic routing protocol on InternetRouter to advertise summarized routers to CentralRouter.
A. a dynamic routing protocol on InternetRouter to advertise summarized routers to CentralRouter.
B. a dynamic routing protocol on CentralRouter to advertise summarized routers to InternetRouter.
C. a static route on InternetRouter to direct traffic that is destined for 172.16.0.0/16 to CentralRouter.
D. a dynamic routing protocol on InternetRouter to advertise all routes to CentralRouer.
E. a dynamic routing protocol on CentralRouer to advertise all routes to InternetRouter
F. a static, default route on CentralRouter that directs traffic to InternetRouter.
Answer: C F
A. an OSPF update for network 192.168.0.0/16
B. a static router to network 192.168.10.0/24
C. a static router to network 192.168.10.0/24 with a local serial interface configured as the next hop
D. a RIP update for network 192.168.10.0/24
E. a directly connected interface with an address of 192.168.10.254/24
F. a default route with a next hop address of 192.168.10.1
Answer: E
A. link bandwidth
B. hop count
C. link cost
D. administrative distance
E. link delay
Answer: D
A. RIPV1 and OSPF are classless routing protocols.
B. Classful routing protocols send the subnet mask in routing updates.
C. Automatic summarization at classful boundaries can cause problems on discontiguous networks.
D. EIGRP and OSPF are classful routing protocols and summarize routes by default.
Answer: C
A. Security increases because only the network administrator may change the routing tables.
B. Configuration complexity decreases as network size increases.
C. Routing updates are automatically sent to neighbors.
D. Route summarization is computed automatically by the router.
E. Routing traffic load is reduced when used in stub network links.
F. An efficient algorithm is used to build routing tables using automatic updates.
G. Routing tables adapt automatically to topology changes.
Answer: A E
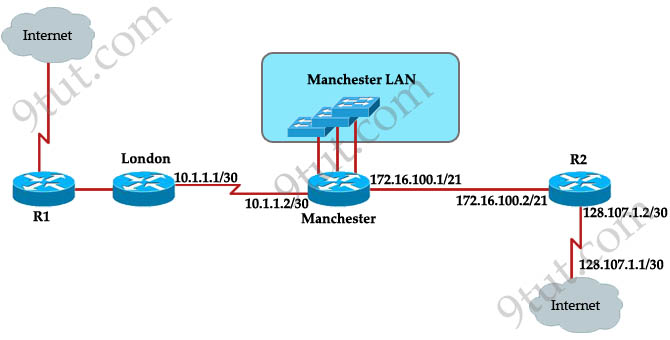 A. ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.100.2
A. ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.100.2
B. ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 128.107.1.1
C. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 128.107.1.1
D. ip route 0.0.0.00.0:0:0 172.16.100.1
E. ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 172.16.100.2
F. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.100.2
Answer: F
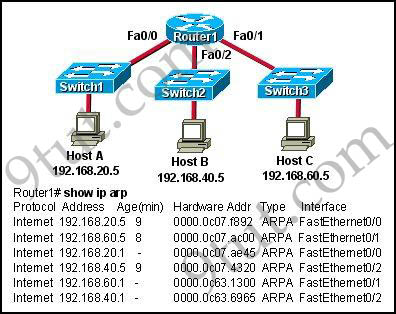
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit. Host A is to send data to Host B. How will
Router1 handle the data frame received from Host A? (Choose three)
B. Router1 will strip off the source IP address and replace it with the IP address on the forwarding FastEthernet interface.
C. Router1 will strip off the destination MAC address and replace it with the MAC address of Host B.
D. Router1 will strip off the destination IP address and replace it with the IP address of Host B.
E. Router1 will forward the data frame out interface FastEthernet0/1.
F. Router1 will forward the data frame out interface FastEthernet0/2.
Answer: A C F
Explanation
While transferring data through many different networks, the source
and destination IP addresses are not changed. Only the source and
destination MAC addresses are changed. So in this case, Host A will use
the IP address of Host B and the MAC address of Fa0/0 interface to send
data. When the router receives this data, it replaces the source MAC
address with it own Fa0/2 interface’s MAC address and replaces the
destination MAC address with Host B’s MAC address before sending to Host
B -> A, C and F are correct.
Question 2
What is an appropriate use of a default route?A. to provide routing to a local web server
B. to provide routing from an ISP to a stub network
C. to provide routing that will override the configured dynamic routing protocol
D. to provide routing to a destination that is not specified in the routing table and which is outside the local network
Answer: D
Explanation
Default routes are used to direct packets addressed to networks not
explicitly listed in the routing table. An example of default route is:Router(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.1
(Notice that the network address of default route is 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0)
Question 3
A medium-sized company has a Class C IP address. It has two Cisco routers and one non-Cisco router.All three routers are using RIP version 1.
The company network is using the block of 198.133.219.0/24.
The company has decided it would be a good idea to split the network into three smaller subnets and create the option of conserving addresses with VLSM.
What is the best course of action if the company wants to have 40 hosts in each of the three subnets?
A. Convert all the routers to EIGRP and use 198.133.219.32/27, 198.133.219.64/27, and 198.133.219.92/27 as the new subnetworks.
B. Maintain the use of RIP version 1 and use 198.133.219.32/27, 198.133.219.64/27, and 198.133.219.92/27 as the new subnetworks.
C. Convert all the routers to EIGRP and use 198.133.219.64/26, 198.133.219.128/26, and 198.133.219.192/26 as the new subnetworks.
D. Convert all the routers to RIP version 2 and use 198.133.219.64/26, 198.133.219.128/26, and 198.133.219.192/26 as the new subnetworks.
E. Convert all the routers to OSPF and use 198.133.219.16/28, 198.133.219.32/28, and 198.133.219.48/28 as the new subnetworks.
F. Convert all the routers to static routes and use 198.133.219.16/28, 198.133.219.32/28, and 198.133.219.48/28 as the new subnetworks.
Answer: D
Explanation
RIP version 1 does not support VLSM so we have to convert into RIPv2, OSPF or EIGRP -> B is not correct.But EIGRP is a Cisco-proprietary routing protocol so it can not be used in a non-Cisco router -> A and C are not correct.
To support 40 hosts per subnet we need a subnet mask of /26 or lower (which leaves 6 bits 0 and 26 = 64 > 40 hosts). Therefore a subnet mask of /28 is not suitable in this case -> E & F are not correct.
Question 4
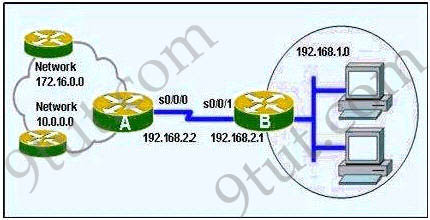
Refer to the exhibit. Which command will created a default route on RouterB to reach all networks beyond RouterA?
B. ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.1
C. ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 s0/0/0
D. ip route 10:0.0.0 255.255.255.0 s0/0/0
E. ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.2
Answer: A
Explanation
Notice that in the static (or default) route we need to specify the
exit-interface (local on that router) or the next-hop IP address (of a
directly connected router) -> A is correct.
Question 5
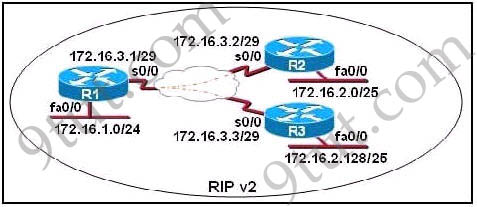
Refer to the exhibit. S0/0 on R1 is configured as a multipoint
interface to communicate with R2 and R3 in the hub-and-spoke Frame Relay
topology. While testing this configuration, a technician notes that
pings are successfully from hosts on the 172.16.1.0/24 network to hosts
on both the 172.16.2.0/25 and 172.16.0.2.128/25 networks. However, pings
between hosts on the 172.16.2.0/25 and 172.16.2.128/25 network are not
successful. What could explain this connectivity problem?
B. The RIPv2 dynamic routing protocol cannot be used across a Frame Relay network.
C. Split horizon is preventing R2 from learning about the R3 networks and R3 from learning about R2 networks.
D. The 172.16.2.0/25 and 172.16.2.128/25 networks are overlapping networks that can be seen by R1, but not between R2 and R3.
E. The 172.16.3.0/29 network used on the Frame Relay links is creating a discontiguous network between the R2 and R3 router subnetworks.
Answer: C
Explanation
The split horizon rule states “a router never sends information about
a route back in same direction which is original information came”. In
this case it means whenR3 sends update to R1 via s0/0, R1 does not send
any update for same network out of interface s0/0. To solve this problem
we can configure sub-interfaces on s0/0 or explicitly allow the update
to be sent back on the same interface.
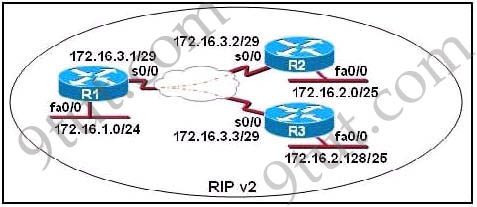
Question 6
S0/0 on R1 is configured as a multipoint interface to communicate
with R2 and R3 in the hub-and-spoke Frame Relay topology shown in the
exhibit. Originally, static routes were configured between these routers
to successfully route traffic between the attached networks. What will
need to be done in order to use RIPv2 in place of the static routes?
B. Dynamic routing protocols such as RIPv2 cannot be used across Frame Relay networks.
C. Configure the S0/0 interface on R1 as two subinterfaces and configure point-to-point links to R2 and R3.
D. Change the 172.16.2.0/25 and 172.16.2.128/25 subnetworks so that at least two bits are borrowed from the last octet.
E. Change the network address configuration to eliminate the discontiguous 172.16.2.0/25 and 172.16.2.128/25 subnetwork.
Answer: C
Explanation
Same as Question 5
Question 7
Refer to the exhibit. A network associate has configured the
internetwork that is shown in the exhibit, but has failed to configure
routing properly.
A.
HQ(config)# ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.5
Branch(config) # ip route 172.16.25.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.6
B.
HQ(config)# router rip
HQ(config-router)# network 192.168.2.0
HQ(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0
Branch(config)# router rip
Branch(config-router) # network 192.168.1.0
Branch(config-router)# network 192.168.2.0
C.
HQ(config)# router eigrp 56
HQ(config-router)# network 192.168.2.4
HQ(config-router)# network 172.16.25.0
Branch(config)# router eigrp 56
Branch(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0
Branch(config-router) # network 192.168.2.4
D.
HQ(config)# router ospf 1
HQ(config-router)# network 192.168.2.4 0.0.0.3 area 0
HQ(config-router)# network 172.16.25.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Branch(config)# router ospf 1
Branch(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Answer: A
Explanation
By configuring static route, we can minimize the router processing and WAN bandwidth.
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator requires easy
configuration options and minimal routing protocol traffic. Which two
options provide adequate routing table information for traffic that
passes between the two routers and satisfy the requests of the network
administrator?(choose two)
B. a dynamic routing protocol on CentralRouter to advertise summarized routers to InternetRouter.
C. a static route on InternetRouter to direct traffic that is destined for 172.16.0.0/16 to CentralRouter.
D. a dynamic routing protocol on InternetRouter to advertise all routes to CentralRouer.
E. a dynamic routing protocol on CentralRouer to advertise all routes to InternetRouter
F. a static, default route on CentralRouter that directs traffic to InternetRouter.
Answer: C F
Question 9
A router receives information about network 192.168.10.0/24 from
multiple sources. What will the router consider the most reliable
information about the path to that network?A. an OSPF update for network 192.168.0.0/16
B. a static router to network 192.168.10.0/24
C. a static router to network 192.168.10.0/24 with a local serial interface configured as the next hop
D. a RIP update for network 192.168.10.0/24
E. a directly connected interface with an address of 192.168.10.254/24
F. a default route with a next hop address of 192.168.10.1
Answer: E
Question 10
Which parameter can be tuned to affect the selection of a static route as a backup when a dynamic protocol is also being used?A. link bandwidth
B. hop count
C. link cost
D. administrative distance
E. link delay
Answer: D
Question 11
Which statement is true, as relates to classful or classless routing?A. RIPV1 and OSPF are classless routing protocols.
B. Classful routing protocols send the subnet mask in routing updates.
C. Automatic summarization at classful boundaries can cause problems on discontiguous networks.
D. EIGRP and OSPF are classful routing protocols and summarize routes by default.
Answer: C
Question 12
Which two are advantages of static routing when compared to dynamic routing? (choose two)A. Security increases because only the network administrator may change the routing tables.
B. Configuration complexity decreases as network size increases.
C. Routing updates are automatically sent to neighbors.
D. Route summarization is computed automatically by the router.
E. Routing traffic load is reduced when used in stub network links.
F. An efficient algorithm is used to build routing tables using automatic updates.
G. Routing tables adapt automatically to topology changes.
Answer: A E
Question 13
The speed of all serial links is E1 and the speed of the all other
links is 100Mb/s. A static route will be established on the Manchester
router to direct traffic toward to the internet over the most direct
path available. What configuration of the Manchester router will
establish a route toward to the internet for traffic from workstation on
the Manchester LAN?
B. ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.252 128.107.1.1
C. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 128.107.1.1
D. ip route 0.0.0.00.0:0:0 172.16.100.1
E. ip route 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 172.16.100.2
F. ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.100.2
Answer: F
Explanation
Maybe “the most direct path available” here means via R2 because it
is directly connected with the Internet while the London path needs to
go through R1. So we need a command to send traffic to R2 and the
correct command is “ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.100.2″.
No comments:
Post a Comment