Here you will find answers to EIGRP Questions – Part 2
Note: If you are not sure about EIGRP, please read my EIGRP tutorial.
A. the OSPF route
B. the EIGRP route
C. the RIPv2 route
D. all three routes
E. the OSPF and RIPv2 routes
Answer: B
 Question 3
Question 3
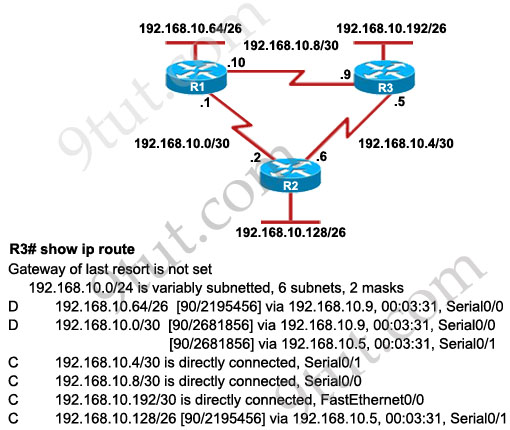
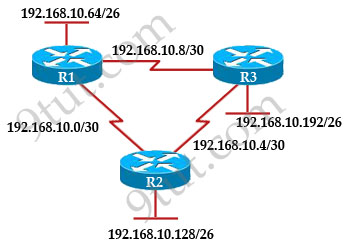
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the exhibited routing table, how will packets from a host within the 192.168.10.192/26 LAN be forwarded to 192.168.10.1?
 A. The router will forward packets from R3 to R2 to R1
A. The router will forward packets from R3 to R2 to R1
B. The router will forward packets from R3 to R1
C. The router will forward packets from R3 to R1 to R2
D. The router will forward packets from R3 to R2 to R1 AND from R3 to R1
Answer: D
 R3# show ip route
R3# show ip route
Gateway of last resort is not set
192 168.10.0/24 is variably subnetted, 6 subnets, 2 masks
D 192.168.10.64/26 [90/2195456] via 192.168.10.9, 00:03:31, Serial0/0
D 192.168.10.0/30 [90/2681856] via 192.168.10.9, 00:03:31, Serial0/0
C 192.168.10.4/30 is directly connected, Serial0/1
C 192.168.10.8/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0
C 192.168.10.192/26 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
D 192.168.10.128/26 [90/2195456] via 192.168.10.5,00:03:31, Serial0/1
A. The path of the packets will be R3 to R2 to R1.
B. The path of the packets will be R3 to R1 to R2.
C. The path of the packets will be both R3 to R2 to R1 and R3 to R1.
D. The path of the packets will be R3 to R1
Answer: D
A. forwards the received packet out the Serial0/0 interface
B. forwards a packet containing an EIGRP advertisement out the Serial0/1 interface
C. forwards a packet containing an ICMP message out the FastEthemet0/0 interface
D. forwards a packet containing an ARP request out the FastEthemet0/1 interface
Answer: C

A. network 172.26.168.0 area 478
B. network 172.26.0.0
C. network 172.26.168.128 0.0.0.127
D. network 172.26.168.128 area 478
Answer: B
A. EIGRP does not support VLSM.
B. The EIGRP network statements are incorrectly configured.
C. The IP addressing on the serial interface of RouterA is incorrect.
D. The routing protocol has summarized on the classful boundary.
E. EIGRP has been configured with an invalid autonomous system number.
Answer: D
Note: EIGRP performs auto-summarization each time it crosses a border between two major networks. For example, RouterA has networks of 172.16.x.x. It will perform auto-summarization when sending over network 10.1.1.0/30, which is in different major network (172.16.0.0/16 and 10.0.0.0/8 are called major networks in this case).
Note: If you are not sure about EIGRP, please read my EIGRP tutorial.
Question 1
A router has learned three possible routes that could be used to
reach a destination network. One route is from EIGRP and has a composite
metric of 20514560. Another route is from OSPF with a metric of 782.
The last is from RIPv2 and has a metric of 4. Which route or routes will
the router install in the routing table?A. the OSPF route
B. the EIGRP route
C. the RIPv2 route
D. all three routes
E. the OSPF and RIPv2 routes
Answer: B
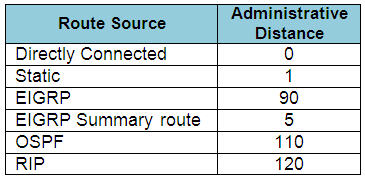
Explanation
When one route is advertised by more than one routing protocol, the
router will choose to use the routing protocol which has lowest
Administrative Distance. The Administrative Distances of popular routing
protocols are listed below:
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the exhibited routing table, how will packets from a host within the 192.168.10.192/26 LAN be forwarded to 192.168.10.1?

B. The router will forward packets from R3 to R1
C. The router will forward packets from R3 to R1 to R2
D. The router will forward packets from R3 to R2 to R1 AND from R3 to R1
Answer: D
Explanation
From the routing table we learn that network 192.168.10.0/30 is
learned via 2 equal-cost paths (192.168.10.9 &192.168.10.5) ->
traffic to this network will be load-balancing.
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit. The company uses EIGRP as the routing protocol.
What path will packets take from a host on 192.168.10.192/26 network to
a host on the LAN attached to router R1?
Gateway of last resort is not set
192 168.10.0/24 is variably subnetted, 6 subnets, 2 masks
D 192.168.10.64/26 [90/2195456] via 192.168.10.9, 00:03:31, Serial0/0
D 192.168.10.0/30 [90/2681856] via 192.168.10.9, 00:03:31, Serial0/0
C 192.168.10.4/30 is directly connected, Serial0/1
C 192.168.10.8/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0
C 192.168.10.192/26 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
D 192.168.10.128/26 [90/2195456] via 192.168.10.5,00:03:31, Serial0/1
A. The path of the packets will be R3 to R2 to R1.
B. The path of the packets will be R3 to R1 to R2.
C. The path of the packets will be both R3 to R2 to R1 and R3 to R1.
D. The path of the packets will be R3 to R1
Answer: D
Explanation
Host on the LAN attached to router R1 belongs to 192.168.10.64/26
subnet. From the output of the routing table of R3 we learn this network
can be reach via 192.168.10.9, which is an IP address in
192.168.10.8/30 network (the network between R1 & R3) -> packets
destined for 192.168.10.64 will be routed from R3 -> R1 -> LAN on
R1.
Question 5
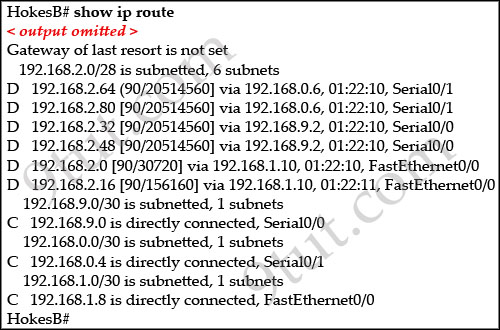
Refer to the exhibit. A packet with a source IP address of
192.168.2.4 and a destination IP address of 10.1.1.4 arrives at the
HokesB router. What action does the router take?
A. forwards the received packet out the Serial0/0 interface
B. forwards a packet containing an EIGRP advertisement out the Serial0/1 interface
C. forwards a packet containing an ICMP message out the FastEthemet0/0 interface
D. forwards a packet containing an ARP request out the FastEthemet0/1 interface
Answer: C
Explanation
When a packet with destination IP address of 10.1.1.4 arrives at
HokesB, it will look up in the routing table to find the most specific
path. In this case no path is found so HokesB must inform to the source
host that the destination is unreachable on the interface it has
received this packet (it is Fa0/0 because the network 192.168.2.0/28 is
learned from this interface). So the best answer here should be C – send
an ICMP message out of Fa0/0.
Question 6
The EIGRP configuration in the Glencoe router uses a single network
statement. From the output shown in the graph would advertise these
networks in EIGRP?
A. network 172.26.168.0 area 478
B. network 172.26.0.0
C. network 172.26.168.128 0.0.0.127
D. network 172.26.168.128 area 478
Answer: B
Explanation
The single “network …” statement used to advertise network
172.26.168.128/26 & 172.26.169.0/26 must cover both of them ->
it is “network 172.26.0.0″. Notice the “network 172.26.168.128
0.0.0.127″ command is valid but it only covers from 172.26.168.128 to
172.26.168.255.
Question 7
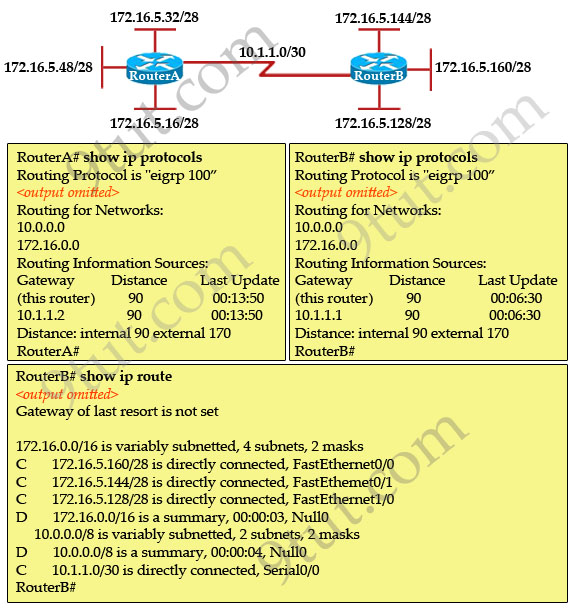
Refer to the exhibit. From RouterA, a network administrator is able
to ping the serial interface of RouterB but unable to ping any of the
subnets attached to RouterB. Based on the partial outputs in the
exhibit, what could be the problem?
A. EIGRP does not support VLSM.
B. The EIGRP network statements are incorrectly configured.
C. The IP addressing on the serial interface of RouterA is incorrect.
D. The routing protocol has summarized on the classful boundary.
E. EIGRP has been configured with an invalid autonomous system number.
Answer: D
Explanation
From the output of “show ip route” command on RouterB, we learn that
RouterB does not learn any networks in RouterA. Also the “172.16.0.0/26
is a summary, 00:00:03, Null0″ line tells us this netwok is summarized.Note: EIGRP performs auto-summarization each time it crosses a border between two major networks. For example, RouterA has networks of 172.16.x.x. It will perform auto-summarization when sending over network 10.1.1.0/30, which is in different major network (172.16.0.0/16 and 10.0.0.0/8 are called major networks in this case).
No comments:
Post a Comment